Certificates
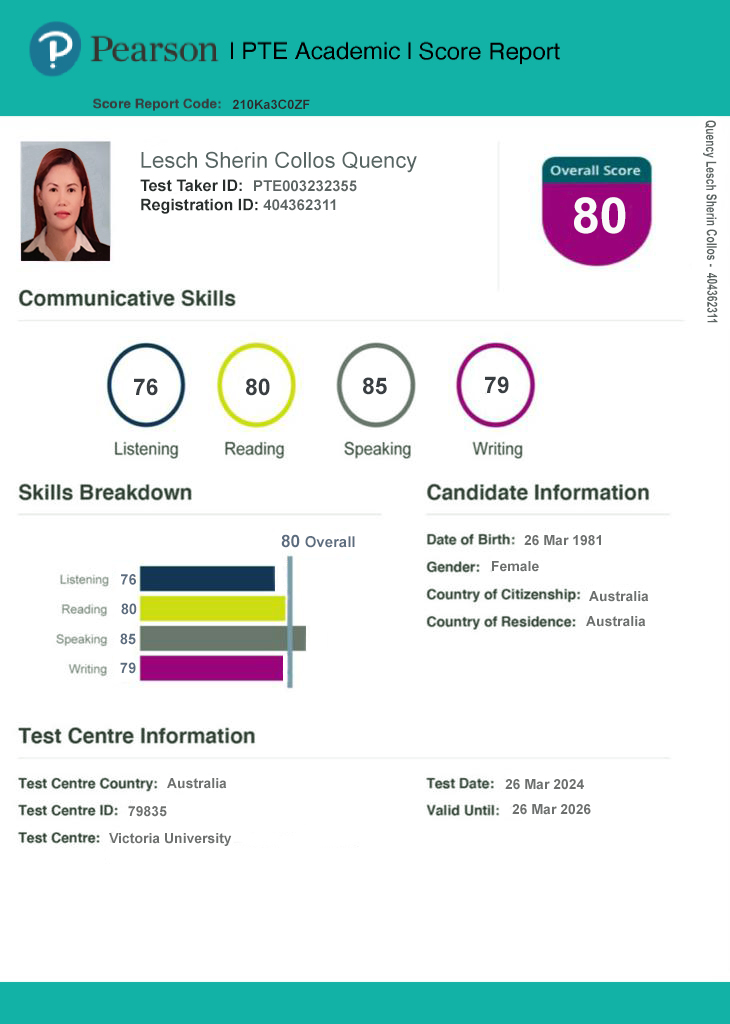
Verifying the legitimacy of a certificate involves several steps to ensure its authenticity. Here’s how you can go about proving that a certificate is legitimate:
Examine Security Features: Many official certificates, such as birth certificates or academic transcripts, include security features to prevent forgery. Look for features such as watermarks, security seals, holograms, or special paper textures. These features are often difficult to replicate and serve as visual cues to the certificate’s authenticity.
Check for Official Signatures and Seals: Official certificates typically bear the signatures of authorized officials or representatives of the issuing authority. Verify that the signatures match those of known officials and that any seals or stamps are consistent with the issuing organization’s standards. You can cross-reference the names of signatories with official lists of authorized personnel if available.
Validate with Issuing Authority: If you have doubts about the legitimacy of a certificate, contact the issuing authority directly to verify its authenticity. This may involve reaching out to government agencies, educational institutions, or professional organizations responsible for issuing the certificate. Provide relevant details such as the certificate number, date of issuance, and any other identifying information to facilitate the verification process.
Use Online Verification Tools: Some organizations offer online verification services for certain types of certificates. These tools allow you to input specific details from the certificate, such as a unique serial number or verification code, to confirm its authenticity. Check if the issuing authority provides such a service and utilize it if available.
Consult Legal or Expert Advice: If you’re unable to verify the legitimacy of a certificate on your own, consider seeking advice from legal professionals or experts in the relevant field. They can provide guidance on the proper procedures for verifying certificates and may be able to assist you in obtaining confirmation from the issuing authority.
Compare with Sample Documents: Obtain sample copies of legitimate certificates issued by the same authority or organization whenever possible. Compare the features, layout, and formatting of the certificate in question with the known authentic samples to identify any discrepancies or irregularities.
Be Wary of Red Flags: Exercise caution if the certificate exhibits any suspicious characteristics, such as spelling errors, unusual formatting, or inconsistencies in information. These could be indicators of forgery or tampering, and further scrutiny may be warranted.
By following these steps and conducting thorough due diligence, you can increase confidence in the legitimacy of a certificate and ensure that it meets the necessary standards for acceptance and recognition.
DRIVERS LICENSE
A driver’s license is a legal document issued by a government authority that grants the holder the privilege to operate a motor vehicle on public roads. It serves as proof that the holder has passed the necessary tests and met the requirements to safely operate a vehicle within a specific jurisdiction. Here are some key points about driver’s licenses:
1. **Issuing Authority**: Driver’s licenses are typically issued by government agencies responsible for regulating motor vehicles and driver licensing within a particular jurisdiction. These agencies may be state-level departments of motor vehicles (DMV), provincial authorities, or other relevant government bodies.
2. **Types of Licenses**: Driver’s licenses may come in various types depending on the type of vehicle the holder is authorized to operate and any restrictions or endorsements they may have. Common types include:
– Standard driver’s license for passenger vehicles
– Commercial driver’s license (CDL) for operating commercial vehicles
– Motorcycle endorsement for operating motorcycles
– Learner’s permit for individuals learning to drive
– Restricted or provisional license for new drivers with certain limitations
3. **Requirements**: To obtain a driver’s license, applicants typically need to meet certain requirements, which may include:
– Passing a written knowledge test on traffic laws and regulations
– Passing a practical driving skills test
– Providing proof of identity, residency, and legal presence in the jurisdiction
– Meeting age requirements (which vary by jurisdiction)
– Completing driver education or training courses, if required
4. **Renewal and Maintenance**: Driver’s licenses are usually valid for a set period, after which they must be renewed to remain valid. Renewal requirements may include passing vision tests, paying renewal fees, and updating personal information. Some jurisdictions also require periodic medical evaluations for certain types of licenses, such as commercial driver’s licenses.
5. **Use and Legal Status**: A driver’s license serves as more than just permission to operate a vehicle—it also serves as a primary form of identification for many purposes, such as opening bank accounts, renting vehicles, or verifying age. It is important to keep the license secure and up-to-date to avoid issues with identification or legal compliance.
6. **International Recognition**: While driver’s licenses are issued by individual jurisdictions, there are often agreements and conventions in place for recognizing licenses from other countries. Many countries honor foreign driver’s licenses for short-term visits, but long-term residents or those planning to drive extensively may need to obtain a local license.
Overall, a driver’s license is a crucial document for individuals who wish to operate motor vehicles legally and responsibly, and it represents a significant milestone in one’s ability to navigate the roadways safely and lawfully.
Any Query
Feel free to contact us and clear your concerns. We have experts who are happy to help you.